Pharmaceuticals Testing Techniques
Pharmaceutical development requires rigorous testing through every stage of research, development, and manufacturing. New formulations must be optimized for stability and bioavailability that enables successful drug delivery and treatment. Lead APIs, excipients, and impurities are carefully measured, and process conditions are created to meet strict quality control standards.
Thermal analysis techniques including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) detect minute transitions caused by a drug’s composition and conditions. Differential scanning calorimetry can detect glass transitions, melting and crystallization while thermogravimetric analysis offers weight change temperature and weight change amount. Rheology is used to measure a drug’s viscosity, which is crucial for delivery of injectables or application of topicals. Sorption analysis (SA) measures a drug’s moisture uptake and related transitions.
Pairing these techniques with intuitive software such as TRIOS Guardian will accelerate pharmaceutical development within your lab. With a broad spectrum of solutions and industry-leading capabilities on each instrument, TA Instruments | Waters offers systems that are sure to enhance your pharmaceutical research and production.

Pharmaceutical Testing Solutions
Pharmaceutical research and discovery is a challenging yet rewarding process that results in the treatment of a disease or clinical condition through new medicine. First, researchers must find a biological target that plays a role in the disease and can be singled out for treatment. During lead discovery, researchers find small molecules or biological therapeutics that they can test as a development candidate. Lead optimization and pre-formulation involve testing and improving crucial characteristics in the lead so it can be properly absorbed for the intended treatment.
Calorimetry is used to characterize minute interactions between macromolecules, while gas analysis and sorption analysis measures the thermal stability and moisture content of pharmaceutical compounds.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Identification of the API or excipient
- Characterization of the API or excipient
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Glass transition (Tg)
- Melting
- Heat of fusion
Temperature Range: -180°C to 725°C
- Water sorption isotherms and kinetic
- Drying and dehydration
- Amorphous content
- Polymorphism
- Hydrate formation and dehydration
Humidity Control Range: 0% to 98% RH
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Thermal stability
- Oxidative stability
Evolved Gas Analysis (EGA)
- Impurity identification
- Composition analysis
Temperature Range: RT to 1500°C
- Binding characterization
- Comparisons of the API or drug product to its target
Temperature Range: 2 °C to 80 °C
Drug formulation and development requires highly accurate characterization of biomolecules to predict their behavior in the body and the efficacy of their treatment. Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and their inactive carriers, or excipients, must be tested for their compatibility and chemical stability. Pharmaceutical developments are also optimized for bioavailability in the body. Rheology helps developers measure the flow behavior of liquids during drug production as well as the viscosity and yield stress of formulations to maintain drug suspension. In topical ointments, emulsion stability is optimized to prevent phase separation.
Sorption Analysis (SA) is used to assess hygroscopicity, amorphous – crystalline phase changes, and hydrate formation.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Eutectic phases and purity
- Phase diagrams
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Compatibility and stability by measuring the change, if any, of the specific heat capacity
- Transitions – Tgs,melting points, heat of fusion
- Detecting and quantifying amorphous content
Temperature Range: -180°C to 550°C
- Evaluate moisture stability by hygroscopicity screening
- Detecting and quantifying amorphous content
- Assessing humidity induced amorphous – crystalline phase changes
- Identify hydrate formation and dehydration
Humidity Control Range: 0% to 98% RH
Processability
- Viscosity Flow Curve
- Shear Thinning
Stability
- Zero-Shear Viscosity
- Yield Stress
- Viscoelastic Properties (G’ and G”)
Temperature Range: -150°C to 600°C
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Thermal and oxidative stability
- Detect and quantify solvents and impurities
- Add EGA (MS or GC/MS) for impurity identification
Temperature Range: 30°C to 1200°C
Once a drug formulation passes initial tests, it moves on to manufacturing and quality control evaluation. Pharmaceutical manufacturers test critical quality attributes (CQAs) and identify the critical material attributes (CMAs) which must remain stable throughout production and until the drug reaches consumers. End user satisfaction also depends upon drug delivery and packaging, which must be tested to eliminate damage to the products. Quality control testing detects any batch-to-batch variation, and manufacture troubleshooting and root cause analysis helps manufacturers identify issues in their process.
Rheology measures critical attributes such as viscosity of injectables as well as viscoelasticity and yield stress of topicals, all which impact drug delivery. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) detect thermal stability and product changes, aiding in process and delivery optimization.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Eutectic purity
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Transitions – Tgs,melting points, heat of fusion
- Detecting and quantifying amorphous content
- Optimize processing conditions
- Quality control
Temperature Range: -180°C to 550°C
Topicals
- Viscosity Flow Curve
- Shear Thinning
- Viscoelastic Modulus (G’, G”)
- Yield Stress
Injectables
- Viscosity Flow Curve
- Viscosity at high shear rate
Temperature Range: -150°C to 600°C
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Detect and quantify solvents and impurities
- Add EGA (MS or GC/MS) for impurity identification
- Quality control
Temperature Range: 30°C to 1200°C
- Assessing storage stability
- Measuring moisture diffusion and permeability
Humidity Control Range: 0% to 98% RH
Successful pharmaceutical products are scaled up to meet consumer demand, which requires rigorous testing and process optimization. Manufacturers must test their process safety and assess risk when designing scaled up manufacturing. Thermal analysis techniques, including DSC, TGA, and Kinetics, measure the thermal stability and phase changes of pharmaceutical products in newly designed manufacturing systems.
Sorption Analysis measures moisture uptake and can help optimize processing systems to minimize negative effects on drug efficacy.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Determine and optimize the process parameters by giving indications about process-induced transformations
- Eutectic purity
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Transitions – Tgs,melting points, heat of fusion
- Lyophilization optimization
Temperature Range: -180°C to 550°C
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Determine compositional accuracy and homogeneity of scaled up mixture
- Impurity detection
- Kinetics
Temperature Range: 30°C to 1200°C
- Research and Discovery
-
Pharmaceutical research and discovery is a challenging yet rewarding process that results in the treatment of a disease or clinical condition through new medicine. First, researchers must find a biological target that plays a role in the disease and can be singled out for treatment. During lead discovery, researchers find small molecules or biological therapeutics that they can test as a development candidate. Lead optimization and pre-formulation involve testing and improving crucial characteristics in the lead so it can be properly absorbed for the intended treatment.
Calorimetry is used to characterize minute interactions between macromolecules, while gas analysis and sorption analysis measures the thermal stability and moisture content of pharmaceutical compounds.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Identification of the API or excipient
- Characterization of the API or excipient
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Glass transition (Tg)
- Melting
- Heat of fusion
Temperature Range: -180°C to 725°C
- Water sorption isotherms and kinetic
- Drying and dehydration
- Amorphous content
- Polymorphism
- Hydrate formation and dehydration
Humidity Control Range: 0% to 98% RH
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Thermal stability
- Oxidative stability
Evolved Gas Analysis (EGA)
- Impurity identification
- Composition analysis
Temperature Range: RT to 1500°C
- Binding characterization
- Comparisons of the API or drug product to its target
Temperature Range: 2 °C to 80 °C
- Drug Formulation and Development
-
Drug formulation and development requires highly accurate characterization of biomolecules to predict their behavior in the body and the efficacy of their treatment. Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and their inactive carriers, or excipients, must be tested for their compatibility and chemical stability. Pharmaceutical developments are also optimized for bioavailability in the body. Rheology helps developers measure the flow behavior of liquids during drug production as well as the viscosity and yield stress of formulations to maintain drug suspension. In topical ointments, emulsion stability is optimized to prevent phase separation.
Sorption Analysis (SA) is used to assess hygroscopicity, amorphous – crystalline phase changes, and hydrate formation.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Eutectic phases and purity
- Phase diagrams
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Compatibility and stability by measuring the change, if any, of the specific heat capacity
- Transitions – Tgs,melting points, heat of fusion
- Detecting and quantifying amorphous content
Temperature Range: -180°C to 550°C
- Evaluate moisture stability by hygroscopicity screening
- Detecting and quantifying amorphous content
- Assessing humidity induced amorphous – crystalline phase changes
- Identify hydrate formation and dehydration
Humidity Control Range: 0% to 98% RH
Processability
- Viscosity Flow Curve
- Shear Thinning
Stability
- Zero-Shear Viscosity
- Yield Stress
- Viscoelastic Properties (G’ and G”)
Temperature Range: -150°C to 600°C
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Thermal and oxidative stability
- Detect and quantify solvents and impurities
- Add EGA (MS or GC/MS) for impurity identification
Temperature Range: 30°C to 1200°C
- Manufacturing, Production, and Quality Control
-
Once a drug formulation passes initial tests, it moves on to manufacturing and quality control evaluation. Pharmaceutical manufacturers test critical quality attributes (CQAs) and identify the critical material attributes (CMAs) which must remain stable throughout production and until the drug reaches consumers. End user satisfaction also depends upon drug delivery and packaging, which must be tested to eliminate damage to the products. Quality control testing detects any batch-to-batch variation, and manufacture troubleshooting and root cause analysis helps manufacturers identify issues in their process.
Rheology measures critical attributes such as viscosity of injectables as well as viscoelasticity and yield stress of topicals, all which impact drug delivery. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) detect thermal stability and product changes, aiding in process and delivery optimization.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Eutectic purity
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Transitions – Tgs,melting points, heat of fusion
- Detecting and quantifying amorphous content
- Optimize processing conditions
- Quality control
Temperature Range: -180°C to 550°C
Topicals
- Viscosity Flow Curve
- Shear Thinning
- Viscoelastic Modulus (G’, G”)
- Yield Stress
Injectables
- Viscosity Flow Curve
- Viscosity at high shear rate
Temperature Range: -150°C to 600°C
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Detect and quantify solvents and impurities
- Add EGA (MS or GC/MS) for impurity identification
- Quality control
Temperature Range: 30°C to 1200°C
- Assessing storage stability
- Measuring moisture diffusion and permeability
Humidity Control Range: 0% to 98% RH
- Scale Up and Engineering
-
Successful pharmaceutical products are scaled up to meet consumer demand, which requires rigorous testing and process optimization. Manufacturers must test their process safety and assess risk when designing scaled up manufacturing. Thermal analysis techniques, including DSC, TGA, and Kinetics, measure the thermal stability and phase changes of pharmaceutical products in newly designed manufacturing systems.
Sorption Analysis measures moisture uptake and can help optimize processing systems to minimize negative effects on drug efficacy.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Determine and optimize the process parameters by giving indications about process-induced transformations
- Eutectic purity
- Polymorphism or polymorphic states
- Transitions – Tgs,melting points, heat of fusion
- Lyophilization optimization
Temperature Range: -180°C to 550°C
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Determine compositional accuracy and homogeneity of scaled up mixture
- Impurity detection
- Kinetics
Temperature Range: 30°C to 1200°C
- Determine and optimize the process parameters by giving indications about process-induced transformations
Pharmaceuticals Webinars
Pharmaceutical Applications
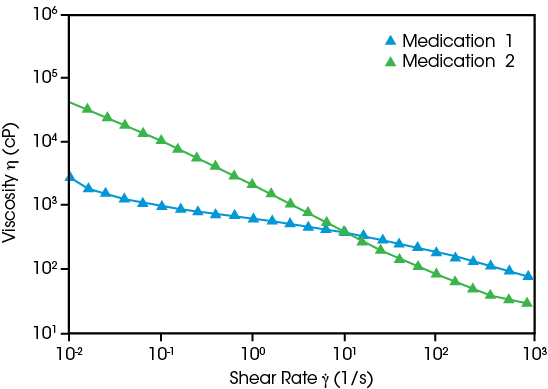
Oral formulations may appear to be simple fluids, but their non-Newtonian flow behavior is vital to their efficacy. Both drug suspensions show higher viscosity at low shear rates, maintaining drug distribution for consistent API concentration. The infant ibuprofen’s shear thinning behavior helps prevent drips during dispensing. Parents can easily administer the medication to a sick infant with accurately controlled dosing.
Discovery Core Rheometer Benefits
- Versatility to characterize wide range of drug delivery systems: oral, injectable, topical
- Torque sensitivity to measure low viscosity formulations
- Perform required measurements of viscosity, viscoelasticity, yield stress and creep-recovery
- Accurately measure semi-solid topicals with textured surface plates to prevent slip
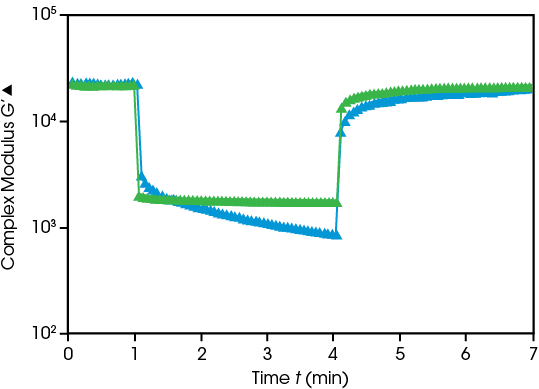
Topical Ointments must balance stability of dispersion with ease of application. Rheology measures how the emulsion structure breaks down and rebuilds over time. The steroid cream and antibiotic ointment show the same modulus at rest, and both decrease under high deformation, with the steroid cream decreasing over time. At rest, antibiotic ointment rapidly rebuilds while steroid cream shows greater time dependence in its recovery.
Discovery Core Rheometer Benefits
- Versatility to characterize wide range of drug delivery systems: oral, injectable, topical
- Torque sensitivity to measure low viscosity formulations
- Perform required measurements of viscosity, viscoelasticity, yield stress and creep-recovery
- Accurately measure semi-solid topicals with textured surface plates to prevent slip
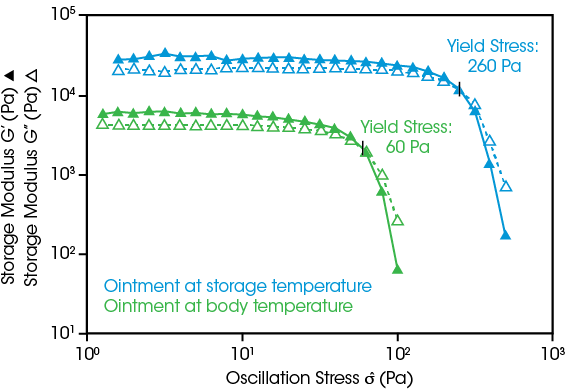
Topical ointments’ yield stress impacts their formulation stability, dispensing from packaging, and behavior after application to the skin. To understand the full range of behavior, yield stress of an ointment is measured at 25 °C (storage temperature) representing the resistance to dispensing, and at 37 °C (body temperature), showing sufficient yield stress is maintained to keep the ointment in place.
Discovery Core Rheometer Benefits
- Versatility to characterize wide range of drug delivery systems: oral, injectable, topical
- Torque sensitivity to measure low viscosity formulations
- Perform required measurements of viscosity, viscoelasticity, yield stress and creep-recovery
- Accurately measure semi-solid topicals with textured surface plates to prevent slip
Blogs
Application Notes
- Apparent Melting: A New Approach to Characterizing Crystalline Structure in Pharmaceutical Materials
- Apparent Melting: A New Approach to Detecting Drug-Excipient Incompatibility
- Amorphous Content of Common Pharmaceutical Materials
- Characterization of Polymorphic Transitions in a Pharmaceutical by DSC and MDSC®
- Quantitative Determination of Amorphous and Crystalline Drug in Polymer Microspheres
- Powder Rheology of Lactose: Impacts of powder morphology on performance of pharmaceutical excipients
- Isothermal Microcalorimetry: Pharmaceutical Applications of Microcalorimetry
- View all Application Notes
















