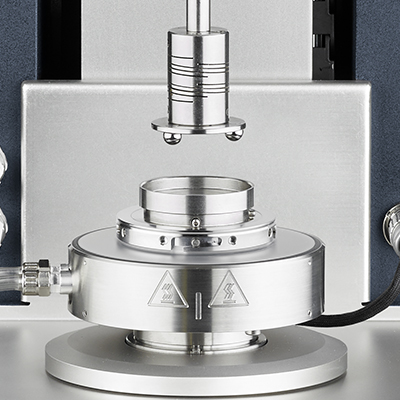

Tribo-Rheometry
Tribology is defined as the study of interacting surfaces undergoing relative motion. The new Tribo-Rheometry Accessory, available for all DHR models, enables the capability to make coefficient of friction measurements between two solid surfaces under dry or lubricated conditions. The unique self-aligning design ensures uniform solid-solid contact and axial force distribution under all conditions. A modular set of standard and novel geometries offers a choice of different contact profiles and direct simulation of end-use conditions. Accurate and precise control of axial force, rotational speed, and temperature inherent to TA Instrument rheometers provides for the best and widest range of friction measurements.
The advanced TRIOS software offers easy setup and control of tribo-rheometry tests and contains a complete set of variables required for data analysis including the coefficient of friction (μ), load force (FL ), friction force (FF ) and Gumbel number (Gu). These may be used to construct Stribeck curves, static friction measurements, or explore specific combinations of temperature, contact force, and motion.
Features and Benefits
- Compatible with Stepped Disposable Peltier Plate and Environmental Test Chamber
- Characterize materials wear and coefficient of friction under dry or lubricated conditions
- Unique self-aligning design for best solid-solid contact
- Modular set of geometries offers choice of contact profiles
- Interchangeable parts for customized substrates
- Automatic software calculation of relevant friction parameters
- Easy installation and removal
Technology

The Tribo-Rheometry Accessory is compatible with both the Stepped Disposable Peltier Plate and the Environmental Test Chamber (ETC) for accurate and stable temperature control for all test geometries. The choice of four standard geometries – Ring on Plate, Ball on Three Plates, Three Balls on Plate, and Ball on Three Balls – meets the diverse requirements of tribology applications and offers a variety of contact profiles. The ring on plate geometry may also be configured as a partitioned ring, which permits the replenishment of lubricant between the two solid surfaces. The accessory’s versatile configurations and easily interchangeable substrates are ideal for studying the effect of friction and long-term wear on materials ranging from automotive components and greases, lubrication in prosthetic devices, and the performance of personal care creams and lotions.
Applications
Friction Measurement of Toothpaste
Friction Measurement of Toothpaste
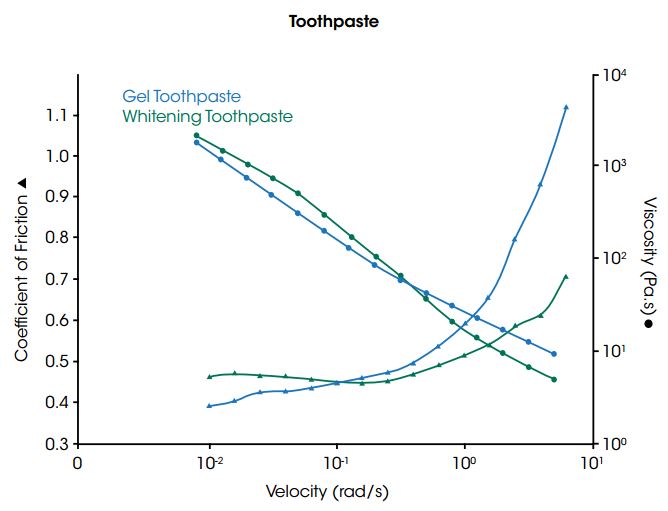
The accompanying figure shows the coefficient of friction profiles of two commercially available toothpastes tested between textured PMMA plates (acting as tooth substitutes) using the ring on plate configuration. The whitening toothpaste, with abrasive particles, has higher friction at low speeds, but the gel toothpaste’s friction profile shows a rapid increase at higher speeds. This behavior can be explained by comparing the flow curves of the two toothpastes – although both materials are shear thinning, the viscosity of whitening toothpaste decreases more rapidly than the gel toothpaste. This results in increased hydrodynamic drag and greater friction at higher rotation speeds.
- Description
-
Tribo-Rheometry
Tribology is defined as the study of interacting surfaces undergoing relative motion. The new Tribo-Rheometry Accessory, available for all DHR models, enables the capability to make coefficient of friction measurements between two solid surfaces under dry or lubricated conditions. The unique self-aligning design ensures uniform solid-solid contact and axial force distribution under all conditions. A modular set of standard and novel geometries offers a choice of different contact profiles and direct simulation of end-use conditions. Accurate and precise control of axial force, rotational speed, and temperature inherent to TA Instrument rheometers provides for the best and widest range of friction measurements.
The advanced TRIOS software offers easy setup and control of tribo-rheometry tests and contains a complete set of variables required for data analysis including the coefficient of friction (μ), load force (FL ), friction force (FF ) and Gumbel number (Gu). These may be used to construct Stribeck curves, static friction measurements, or explore specific combinations of temperature, contact force, and motion.
- Features
-
Features and Benefits
- Compatible with Stepped Disposable Peltier Plate and Environmental Test Chamber
- Characterize materials wear and coefficient of friction under dry or lubricated conditions
- Unique self-aligning design for best solid-solid contact
- Modular set of geometries offers choice of contact profiles
- Interchangeable parts for customized substrates
- Automatic software calculation of relevant friction parameters
- Easy installation and removal
- Technology
-
Technology

The Tribo-Rheometry Accessory is compatible with both the Stepped Disposable Peltier Plate and the Environmental Test Chamber (ETC) for accurate and stable temperature control for all test geometries. The choice of four standard geometries – Ring on Plate, Ball on Three Plates, Three Balls on Plate, and Ball on Three Balls – meets the diverse requirements of tribology applications and offers a variety of contact profiles. The ring on plate geometry may also be configured as a partitioned ring, which permits the replenishment of lubricant between the two solid surfaces. The accessory’s versatile configurations and easily interchangeable substrates are ideal for studying the effect of friction and long-term wear on materials ranging from automotive components and greases, lubrication in prosthetic devices, and the performance of personal care creams and lotions.
- Applications
-
Applications
Friction Measurement of Toothpaste

Friction Measurement of Toothpaste
The accompanying figure shows the coefficient of friction profiles of two commercially available toothpastes tested between textured PMMA plates (acting as tooth substitutes) using the ring on plate configuration. The whitening toothpaste, with abrasive particles, has higher friction at low speeds, but the gel toothpaste’s friction profile shows a rapid increase at higher speeds. This behavior can be explained by comparing the flow curves of the two toothpastes – although both materials are shear thinning, the viscosity of whitening toothpaste decreases more rapidly than the gel toothpaste. This results in increased hydrodynamic drag and greater friction at higher rotation speeds.
- Video
-







